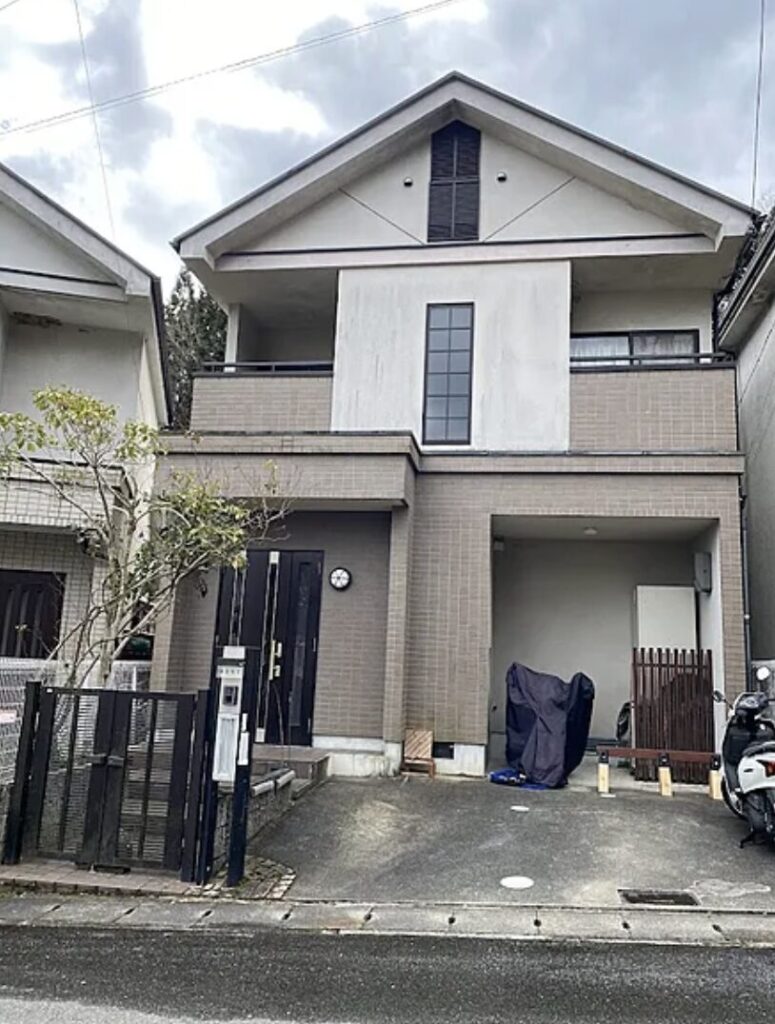
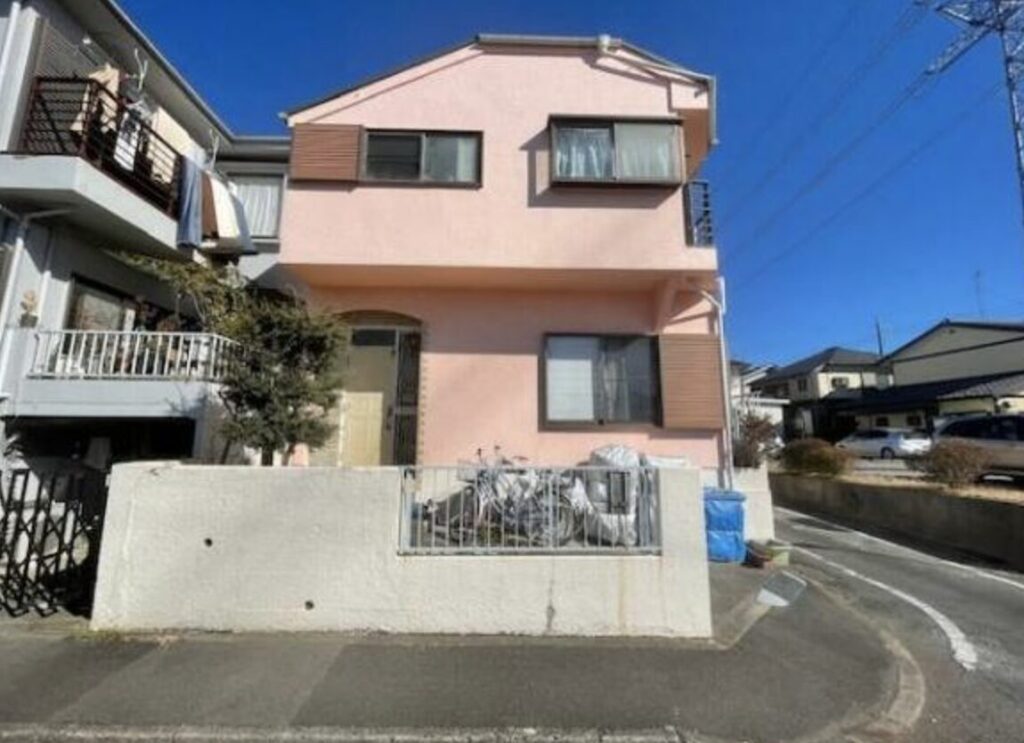
Japan’s hidden residential treasures, known as akiya houses, have been catching the attention of homebuyers and investors alike. These abandoned or vacant houses, which have more than doubled in number over the past 30 years, now stand at a staggering 3.47 million1. In this guide, we’ll cover the essentials for those interested in investing in akiya properties, especially for foreigners who may not be familiar with Japan’s real estate market.
An Overview of Japan’s Abandoned House Problem
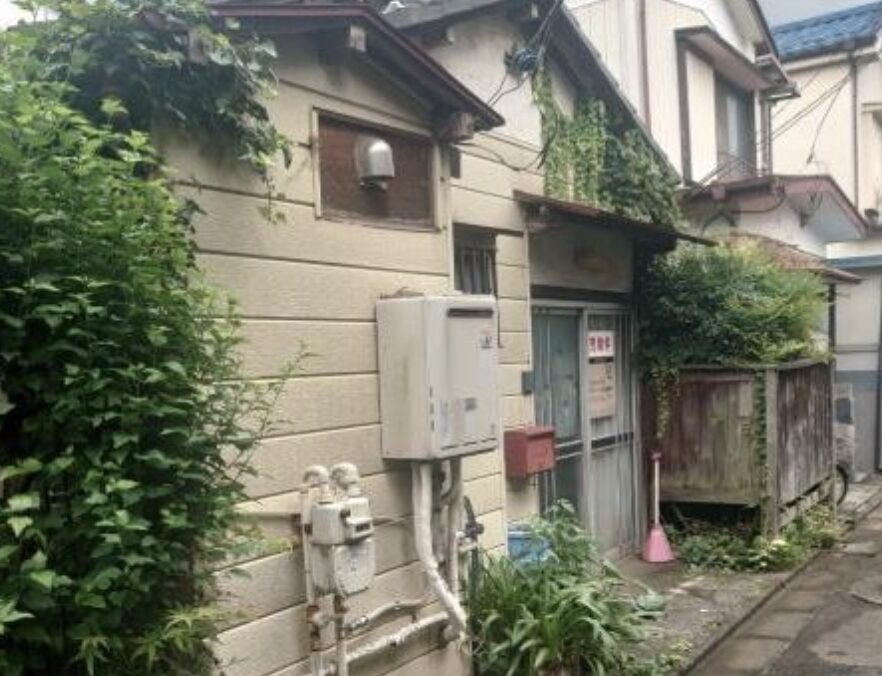
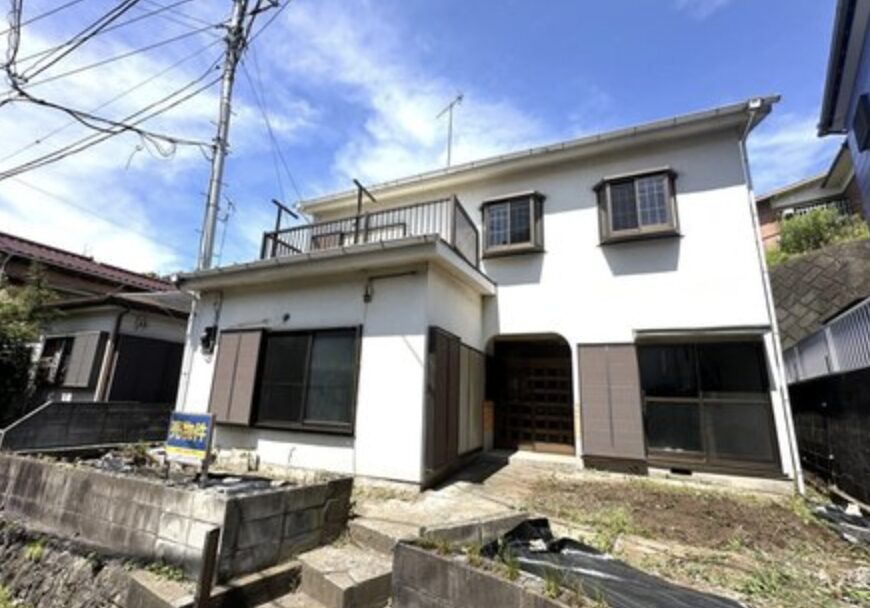
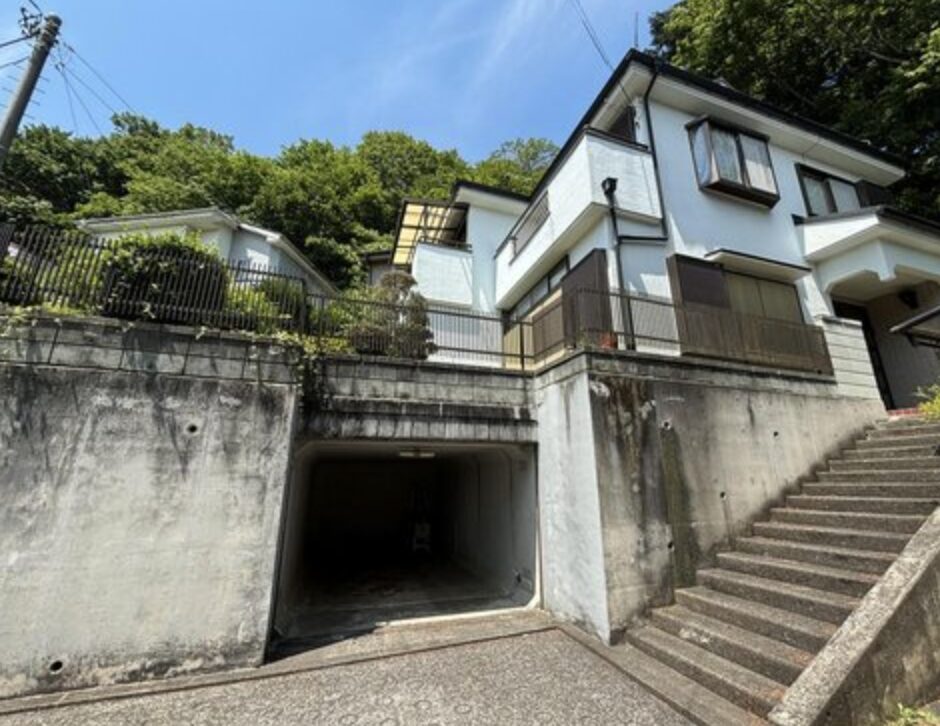
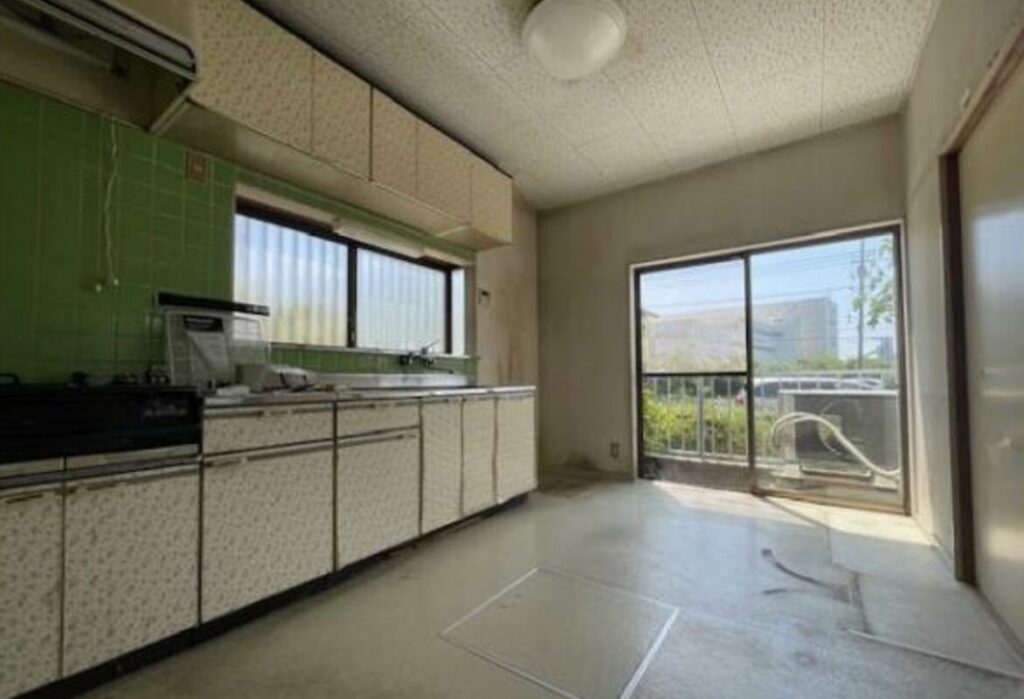
Akiya (空き家) refers to abandoned or vacant houses in Japanese. Sometimes referred to as “ghost houses” by the press, akiya have become an increasingly serious problem over the past few decades. According to the Housing and Land Survey conducted by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the number of abandoned homes increased from approximately 1.82 million in 1998 to 3.47 million in 2018 over a period of 20 years. This trend, often concentrated in the Japanese countryside, presents many hazards, such as building collapse, illegal waste dumping, arson, foul smells, and multiplying pests, to name just a few challenges associated with Japan’s akiya problem.
What Causes Akiya?
Elderly individuals with children may desire to pass their property on to their child after their death. However, the adult children may be working in major cities too far away from the parents’ house (often located in rural Japan) for them to be able to care for the property properly.
Pros and Cons of Moving into an Akiya
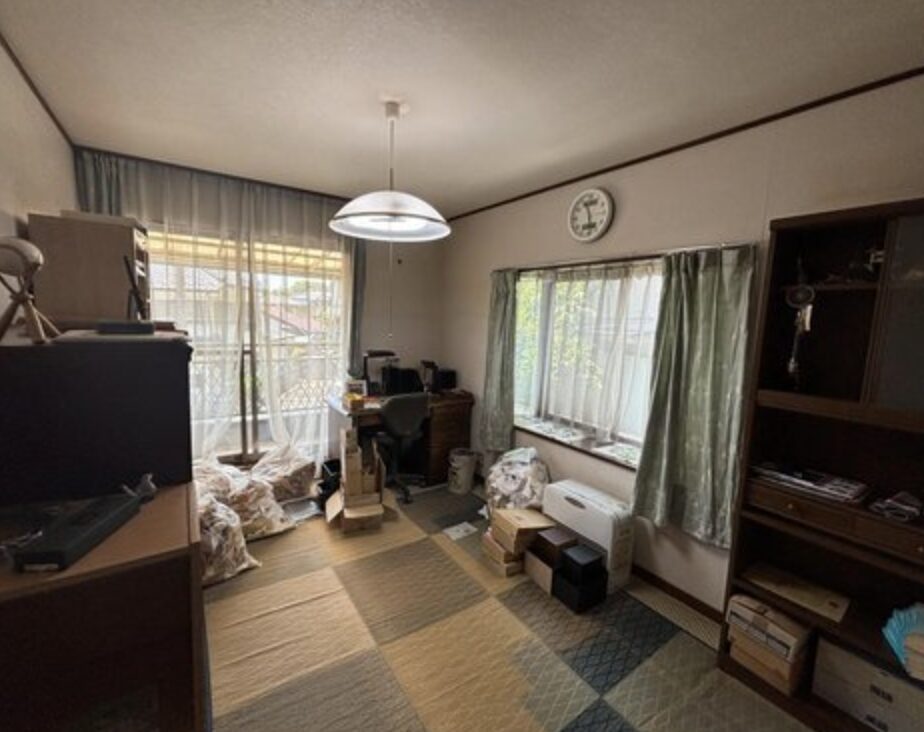
Pros:
- Affordability: Akiya houses are often priced significantly lower than new properties, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers.
- Unique Opportunities: Akiya houses can be renovated and transformed into unique living spaces or creative projects.
- Potential Investment: Some akiya can be turned into profitable vacation rentals or guesthouses.
Cons:
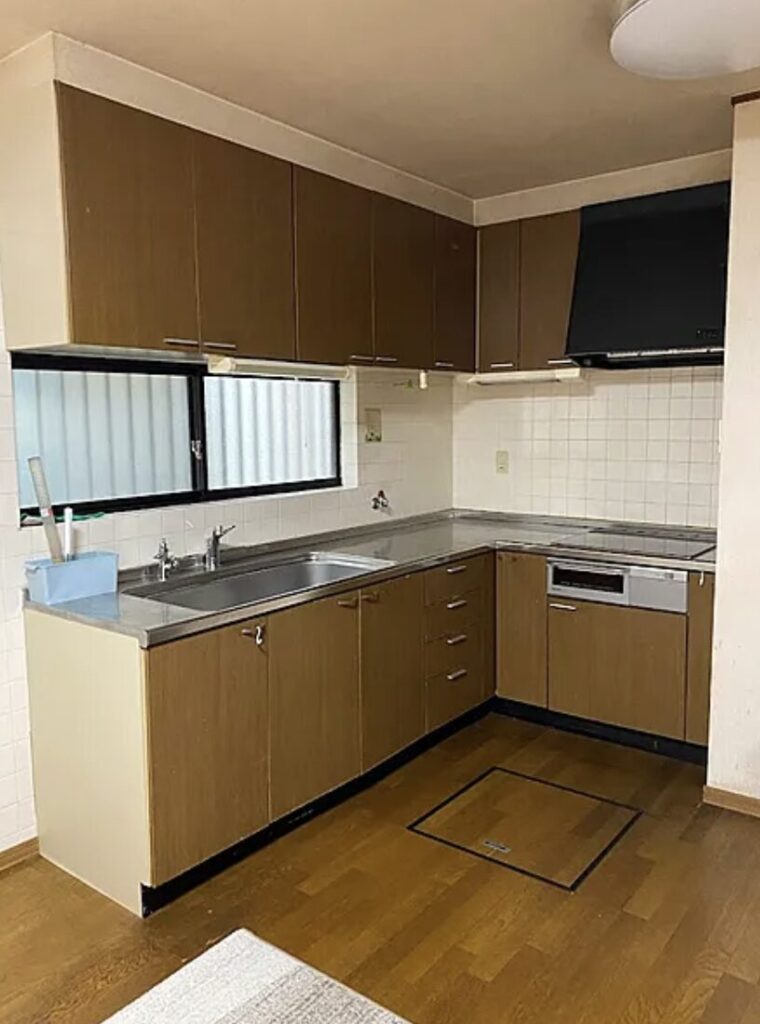
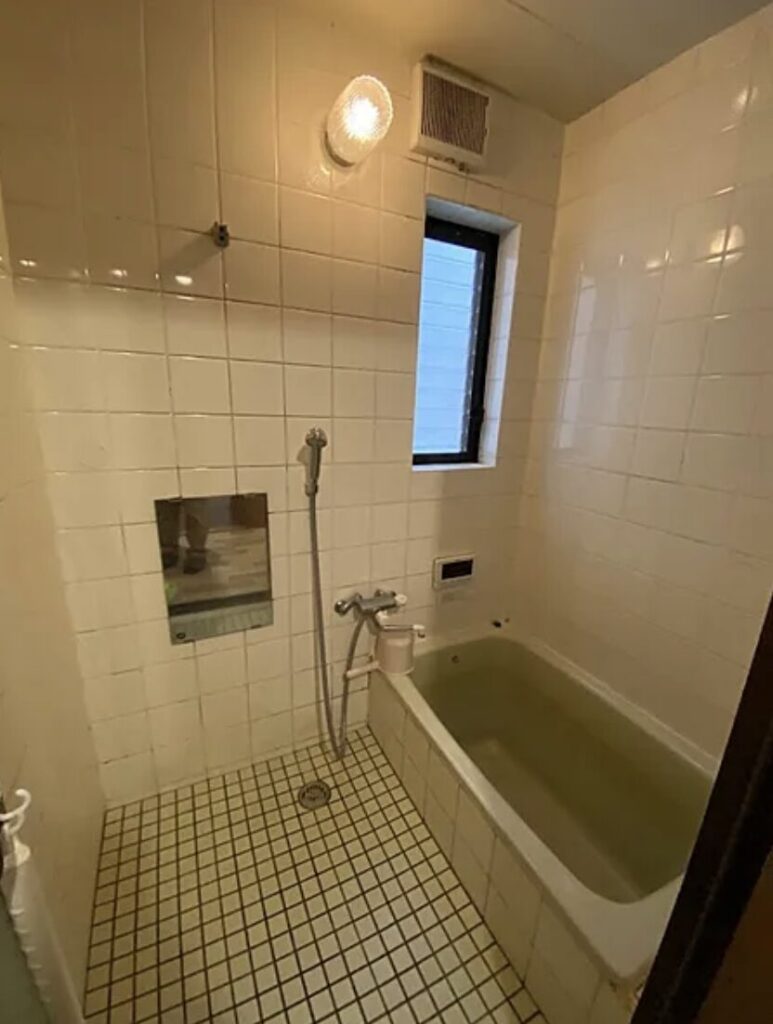
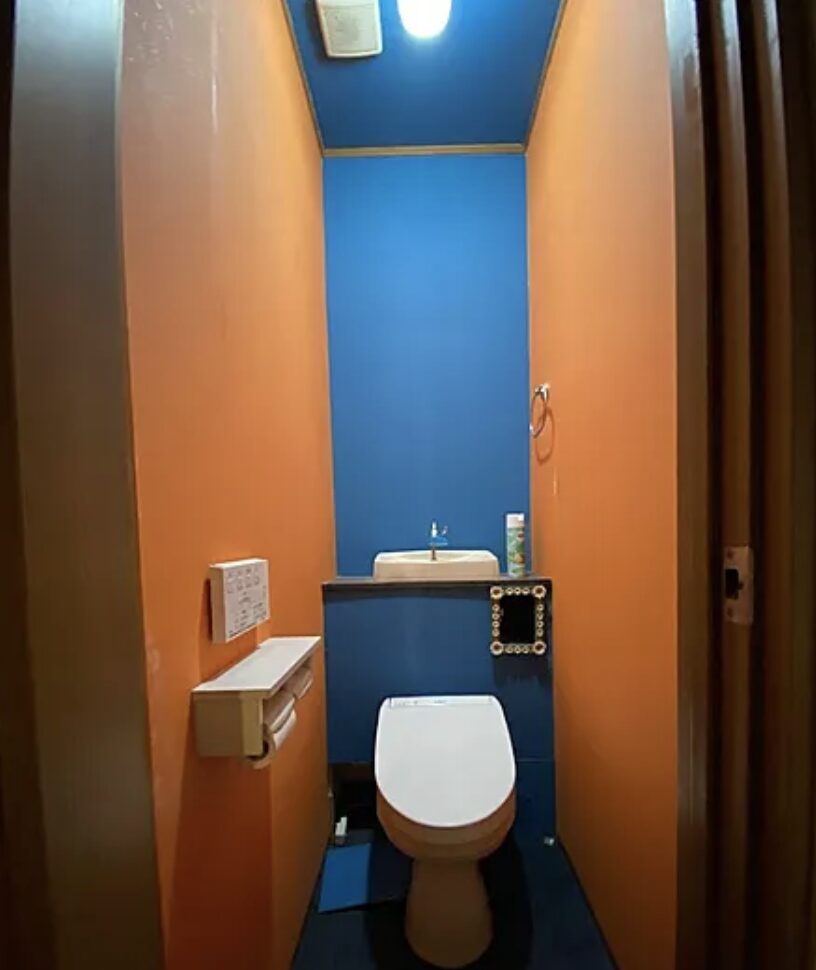
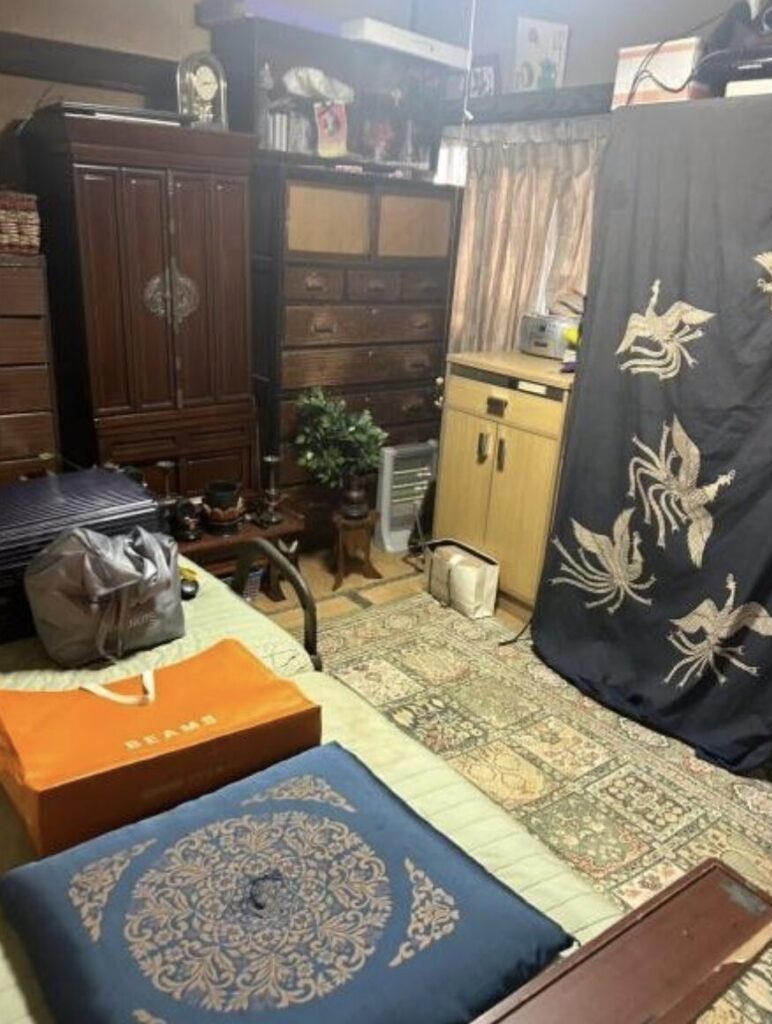
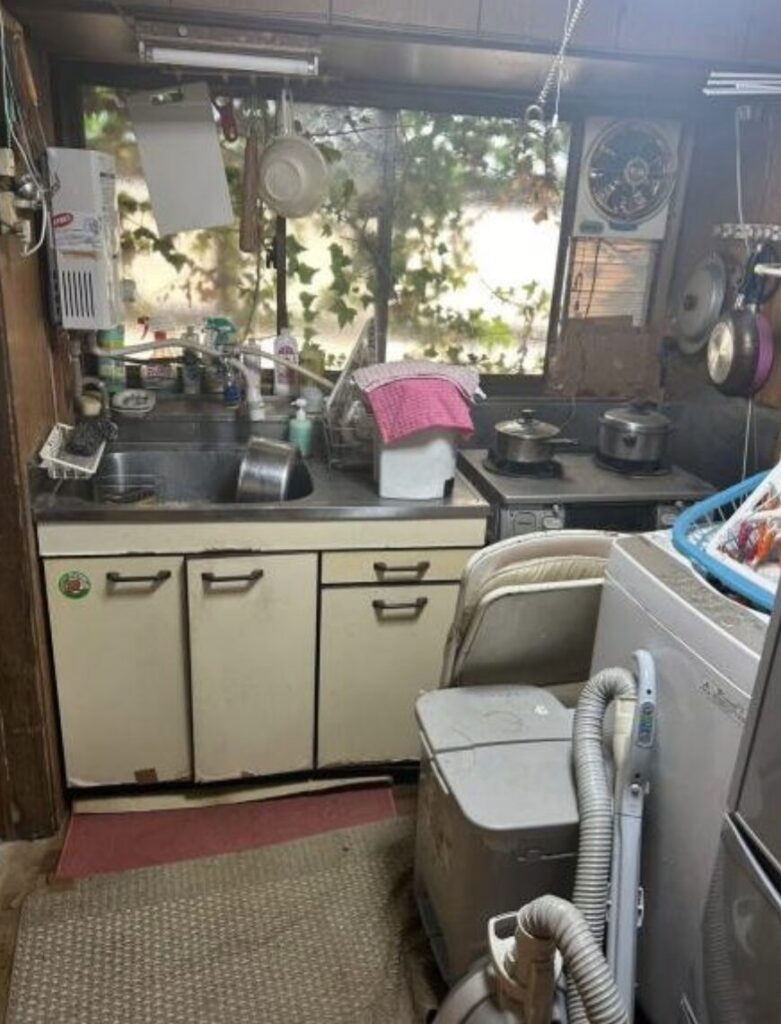
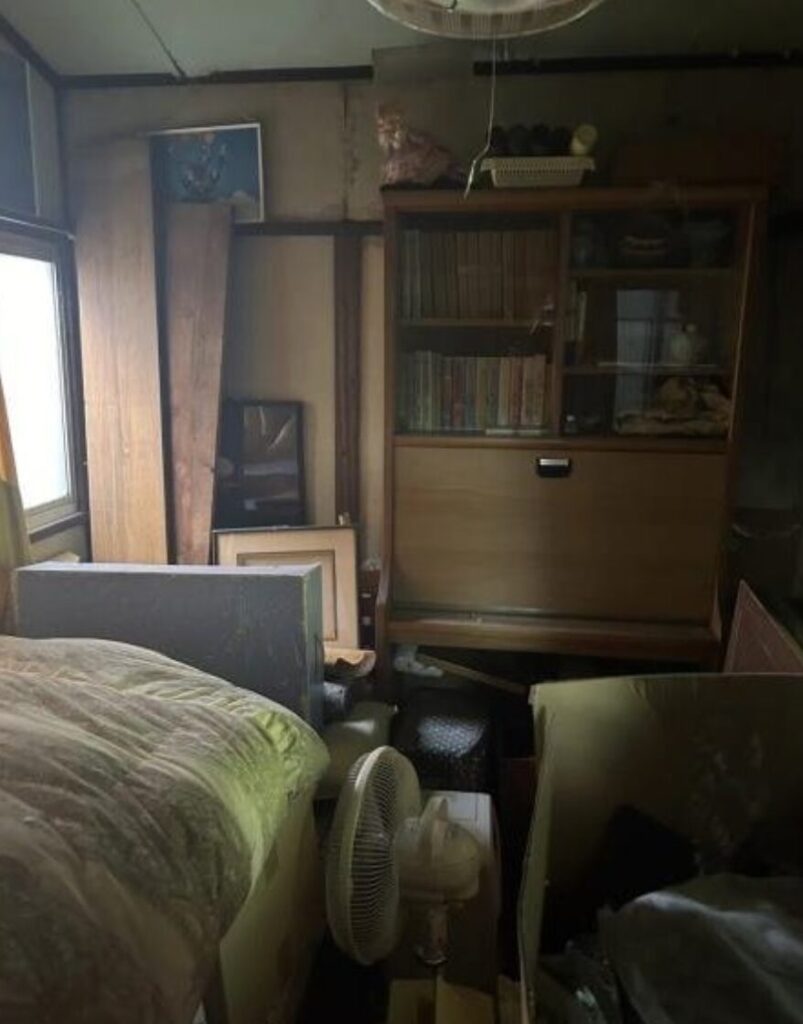
- Condition: Akiya houses may require extensive renovations due to neglect or age.
- Location: Many akiya are in rural areas, which may not suit everyone’s lifestyle.
- Legal and Administrative Challenges: Navigating the paperwork and legal processes can be complex, especially for foreigners.
How to Find Akiya Houses in Japan
- Akiya Banks: Some local governments maintain lists of available akiya properties. Check with local authorities or visit their websites.
- Real Estate Agents: Seek out agents specializing in akiya properties. They can guide you through the process.
- Looking/Asking Yourself: Explore neighborhoods, ask locals, and keep an eye out for vacant houses.
- Japanese Vocabulary: Learn relevant terms to search for akiya online.
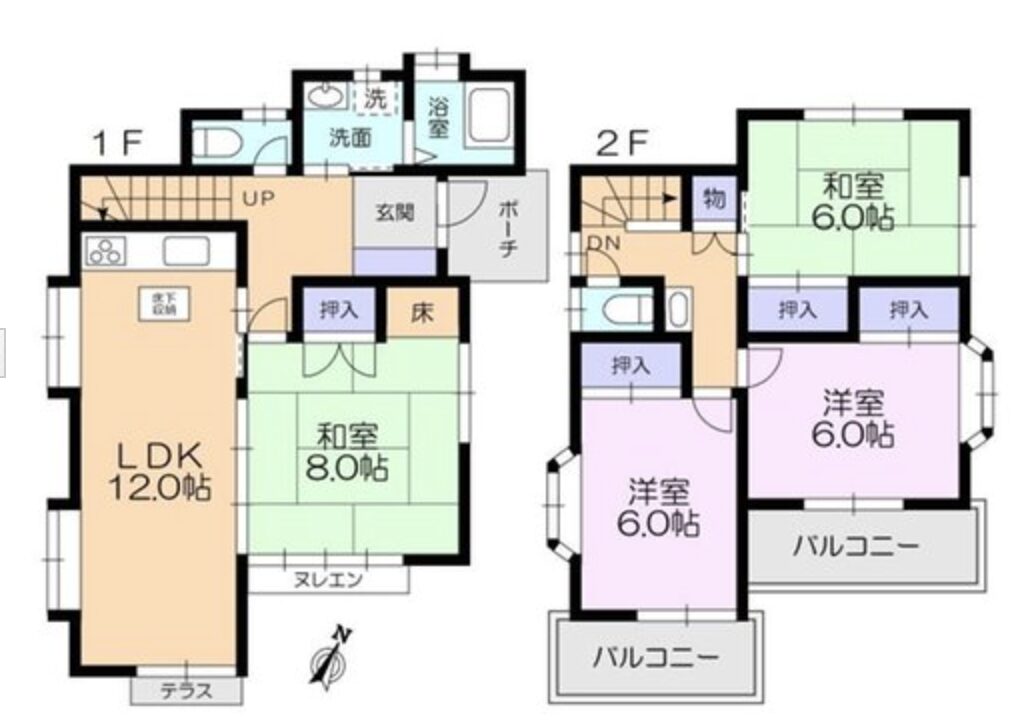
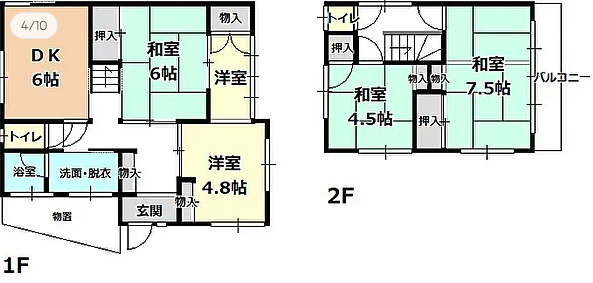
Overview of Purchasing Akiya in Japan
-
List of Documents You May Need (not exhaustive):
- Revenue stamp/handling fee
- Registration and license tax
- Property acquisition tax
- Fixed asset and city planning tax
- Gift tax
-
Tax Deductions Related to Purchasing Akiya:
- Japan’s housing loan deduction
- Japan’s renovation subsidy
In Closing
Investing in akiya houses can be a rewarding venture, but it requires thorough research, understanding of local regulations, and a willingness to tackle renovation challenges. For foreigners interested in Japan’s real estate market, seeking professional advice and assistance is crucial. Remember that while akiya properties offer unique opportunities, they also come with risks and responsibilities1.





































































No comments yet.